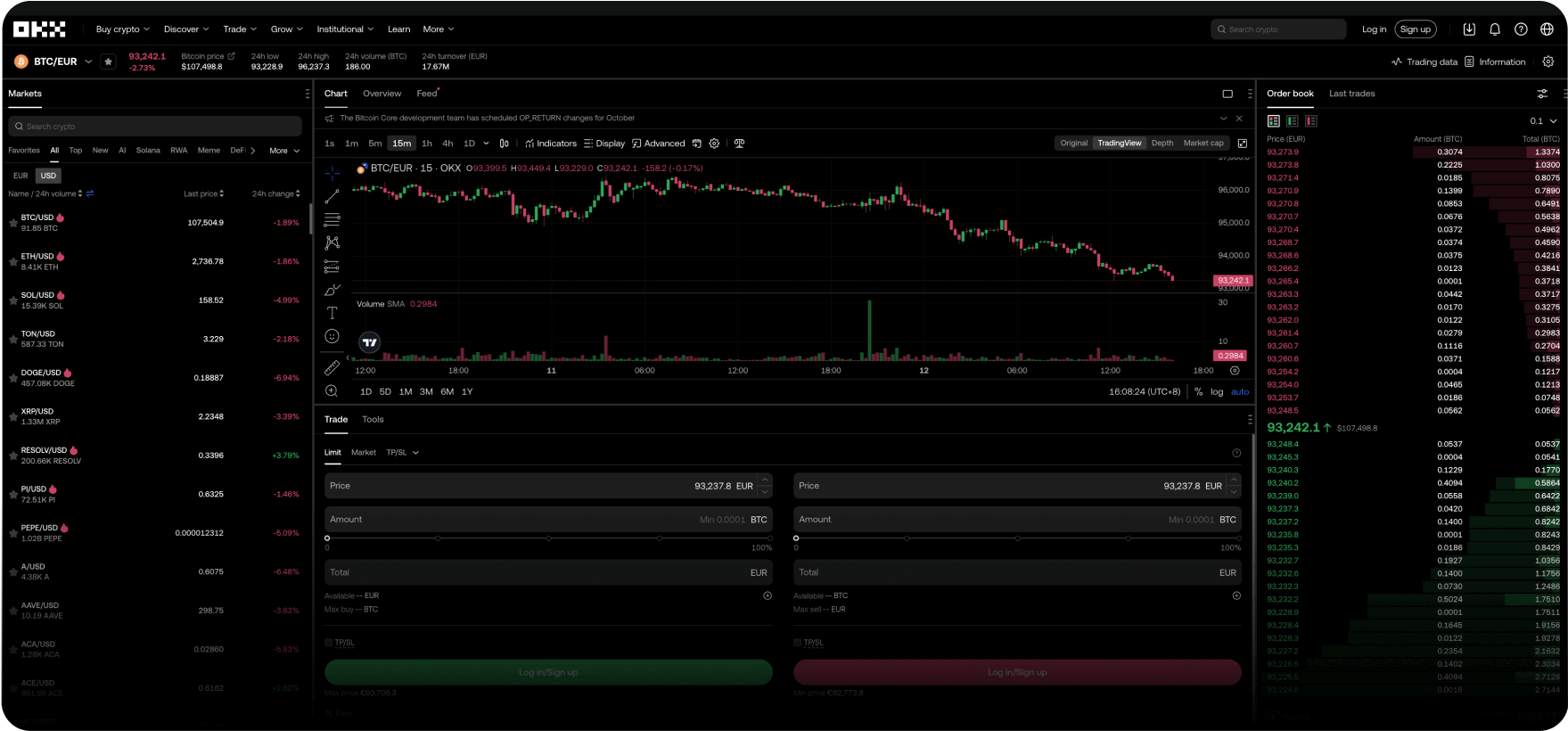
Tu cuenta global en dólares digitales
Disfruta de comisiones más bajas, transacciones más rápidas, las API más potentes y mucho más.
Contigo en cada paso del camino
Desde tu primera operación con criptomonedas hasta convertirte en un trader experto, nosotros te guiaremos durante todo el proceso. Ninguna pregunta es demasiado pequeña. Sin noches en vela. Puedes confiar en las criptos.
El entrenador Pep Guardiola
explica "la disparatada formación del fútbol"
Reescribir el sistema
Te damos la bienvenida a Web3
El snowboarder Scotty James
trae a toda la familia
¿Tienes preguntas? Nosotros, respuestas.
¿Qué productos proporciona OKX?
¿Cómo puedo comprar Bitcoin y otras criptomonedas en OKX?
¿Dónde está la sede de OKX?
¿Pueden las personas residentes en Europa usar OKX?