What Is a Blockchain Oracle?
Blockchain technology has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. However, in order for blockchains to function efficiently, it requires trusted and reliable data sources. This is where blockchain oracles come in.
What Is a Blockchain Oracle
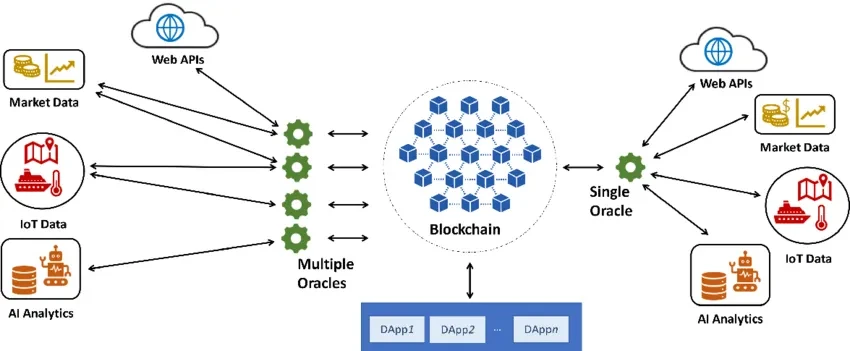
A blockchain oracle acts as a bridge between a blockchain and external data sources. It provides a way for smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts, to interact with real-world data.
Oracles are essential for blockchains to operate efficiently in real-world scenarios. The oracle acts as a trusted data source and verifies it before it is added to the blockchain. The role of the oracle is critical as it ensures that the data added to the blockchain is accurate and tamper-proof, making it an essential component of the blockchain ecosystem.
How Does a Blockchain Oracle Work?
Blockchain oracles act as a bridge between the blockchain and external data sources, providing a way for the blockchain to interact with real-world data. The process of providing data to a blockchain through an oracle is typically done in three steps:
- Data Request: When a smart contract on the blockchain requires data from an external source, it sends a request to the oracle.
- Data Verification: The oracle then verifies the data by using trusted data sources such as APIs, web crawlers, or other off-chain data sources. The data is checked for accuracy and integrity, and if the data is deemed valid, it is then sent back to the smart contract.
- Data Transmission: The data is then transmitted to the blockchain, where it is added as a transaction. This transaction is then verified and validated by the blockchain's nodes, ensuring the accuracy and immutability of the data.
Using an oracle ensures that the blockchain has access to real-world data that it can use to execute smart contracts, which in turn enables a wider range of use cases for blockchain technology.
Types Of Blockchain Oracles
There are two main types of blockchain oracles: centralized and decentralized.
- Centralized Oracles: A centralized oracle is a single entity that provides data to the blockchain. It is often a trusted third party that collects and verifies data from external sources before providing it to the blockchain. Centralized oracles are typically faster and more reliable than decentralized oracles but are also more vulnerable to attacks and manipulation.
- Decentralized Oracles: A decentralized oracle is a network of nodes that work together to provide data to the blockchain. It relies on a consensus mechanism to verify the accuracy and integrity of the data. As a result, decentralized oracles are more secure and resistant to manipulation but can be slower and less reliable than centralized oracles.
In addition to these two categories, there are also a few sub-types of oracles, including:
- Hardware Oracles: These oracles use physical devices such as sensors or RFID chips to provide data to the blockchain.
- Software Oracles: These oracles use software programs to collect data from external sources and provide it to the blockchain.
- Prediction Oracles: These oracles provide data on future events, such as the outcome of a sports game or stock prices.
- Reputation Oracles: These oracles use reputation systems to determine the trustworthiness of data sources and provide data based on that reputation.
The type of oracle used depends on the specific use case and the level of trust and security required.
Blockchain Oracles Trust Issues
While blockchain oracles play a critical role in enabling blockchains to interact with the real world, some trust issues are associated with their use. These issues include:
- Centralization: Centralized oracles are vulnerable to attacks and manipulation as they rely on a single trusted entity to provide data to the blockchain. If this entity is compromised, it can introduce inaccurate or malicious data into the blockchain.
- Data Verification: The accuracy and integrity of the data provided by the oracle depend on the quality of the data sources used and the verification process employed by the oracle. If these sources or processes are unreliable or compromised, it can lead to inaccurate or fraudulent data being added to the blockchain.
- Interoperability: Different blockchains may require different types of data from different sources, making it challenging to standardize the data provided by oracles. This can lead to interoperability issues and limit the usefulness of the data provided by oracles.
To mitigate these trust issues, decentralized oracles can be used, which rely on a network of nodes to verify the accuracy and integrity of the data.
Examples Of Blockchain Oracles
There are several examples of blockchain oracles being used in real-world applications:
- Chainlink: Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides secure and reliable data to smart contracts on various blockchains. It uses a network of nodes to verify the accuracy and integrity of the data and provides data from various sources, including APIs and data feeds.
- Band Protocol: Band Protocol is a decentralized oracle network that provides cross-chain data for various blockchains. It uses a combination of delegated proof-of-stake and proof-of-authority consensus mechanisms to verify the accuracy and integrity of the data.
- Augur: Augur is a decentralized prediction market platform that uses an oracle to provide data on the outcome of events. Users can place bets on the outcome of events such as sports games, elections, and financial markets, and the oracle provides the outcome data to settle the bets.
- Oraclize: Oraclize is a centralized oracle service that provides data to various blockchains, including Ethereum, Bitcoin, and EOS. It uses trusted data sources such as APIs and web crawlers to provide data to smart contracts platforms.
- Harbinger: Harbinger is a decentralized oracle service that provides price data for various digital assets, including cryptocurrencies and stablecoins. It uses a network of nodes to verify the accuracy and integrity of the data and provides data to smart contracts on various blockchains.
Benefits of Blockchain Oracles
Blockchain oracles offer several benefits to the blockchain ecosystem, including:
- Increased functionality for smart contracts: By providing real-world data to smart contracts, blockchain oracles enable more complex and sophisticated smart contracts that can interact with external data and automate processes based on that data.
- Improved accuracy and reliability of data: By verifying data from trusted sources, blockchain oracles ensure that the data added to the blockchain is accurate and tamper-proof, increasing the reliability of the data and reducing the risk of errors or fraud.
- Greater interoperability between blockchains: Blockchain oracles can provide cross-chain data to enable interoperability between blockchains, allowing for seamless exchange of data and assets between blockchain ecosystems.
- New use cases for blockchain technology: Blockchain oracles open up new possibilities for blockchain technology, such as prediction markets, supply chain management, and IoT applications, where real-world data is essential for the blockchain to function effectively.
Blockchain oracles are essential components of the blockchain ecosystem, enabling the blockchain to interact with the real world and enabling new and innovative use cases for blockchain technology.
Challenges With Blockchain Oracles
While blockchain oracles offer several benefits to the blockchain ecosystem, there are also several challenges associated with their use, including:
- Security risks associated with centralized oracles: Centralized oracles are vulnerable to attacks and manipulation, as they rely on a single trusted entity to provide data to the blockchain. If this entity is compromised, it can introduce inaccurate or malicious data into the blockchain.
- Difficulty in verifying data from decentralized oracles: While decentralized oracles can reduce the risk of attacks and manipulation, verifying the accuracy and integrity of the data can be challenging. The consensus mechanism decentralized oracles use must be robust and secure to prevent malicious nodes from introducing fraudulent data.
- Regulatory issues with using third-party data sources: Using third-party data sources can introduce regulatory risks, as these sources may not comply with legal requirements and may introduce inaccurate or fraudulent data into the blockchain.
- Complexity and cost: Implementing a blockchain oracle can be complex and expensive, requiring significant resources and expertise. Additionally, the cost of using oracles can be high, as data providers may charge fees for providing data to the blockchain.
Blockchain developers and users can employ various strategies to address these challenges. For example, developing new technologies and protocols can help reduce the complexity and cost of implementing blockchain oracles, making them more accessible to a wider range of users.
Future of Blockchain Oracles
Blockchain oracles are essential in enabling blockchains to interact with the real world, allowing smart contracts to access real-world data and execute based on that data. They offer several benefits to the blockchain ecosystem, including increased functionality for smart contracts, improved accuracy and reliability of data, greater interoperability between different blockchains, and new use cases for blockchain technology.
However, there are several challenges associated with their use. These include security risks associated with centralized oracles, difficulty verifying data from decentralized oracles, regulatory issues with using third-party data sources, and complexity and cost. As blockchain technology matures, we expect to see more innovative uses of blockchain oracles. This development will also bring about the creation of new technologies and protocols to address the associated challenges.
FAQs
What Is Oracle Used for in Blockchain?
An Oracle is a middleware that bridges a blockchain and external data sources in a blockchain. It provides a way for smart contracts to interact with real-world data, enabling more sophisticated and complex smart contract functionality.
What Is the First Blockchain Oracle?
The first blockchain oracle was most likely the Bitcoin oracle, developed in 2012. It was a simple implementation that provided price data for Bitcoin from external data sources.
What Is an Example of a Blockchain Oracle?
Chainlink is one example of a blockchain oracle widely used in the blockchain ecosystem. It is a decentralized oracle network that provides secure and reliable data to smart contracts on various blockchains.
What Is the Best Blockchain Oracle?
There is no one "best" blockchain oracle, as the choice of oracle depends on the specific use case and the level of trust and security required. Some popular blockchain oracles include Chainlink, Band Protocol, Augur, and Oraclize.