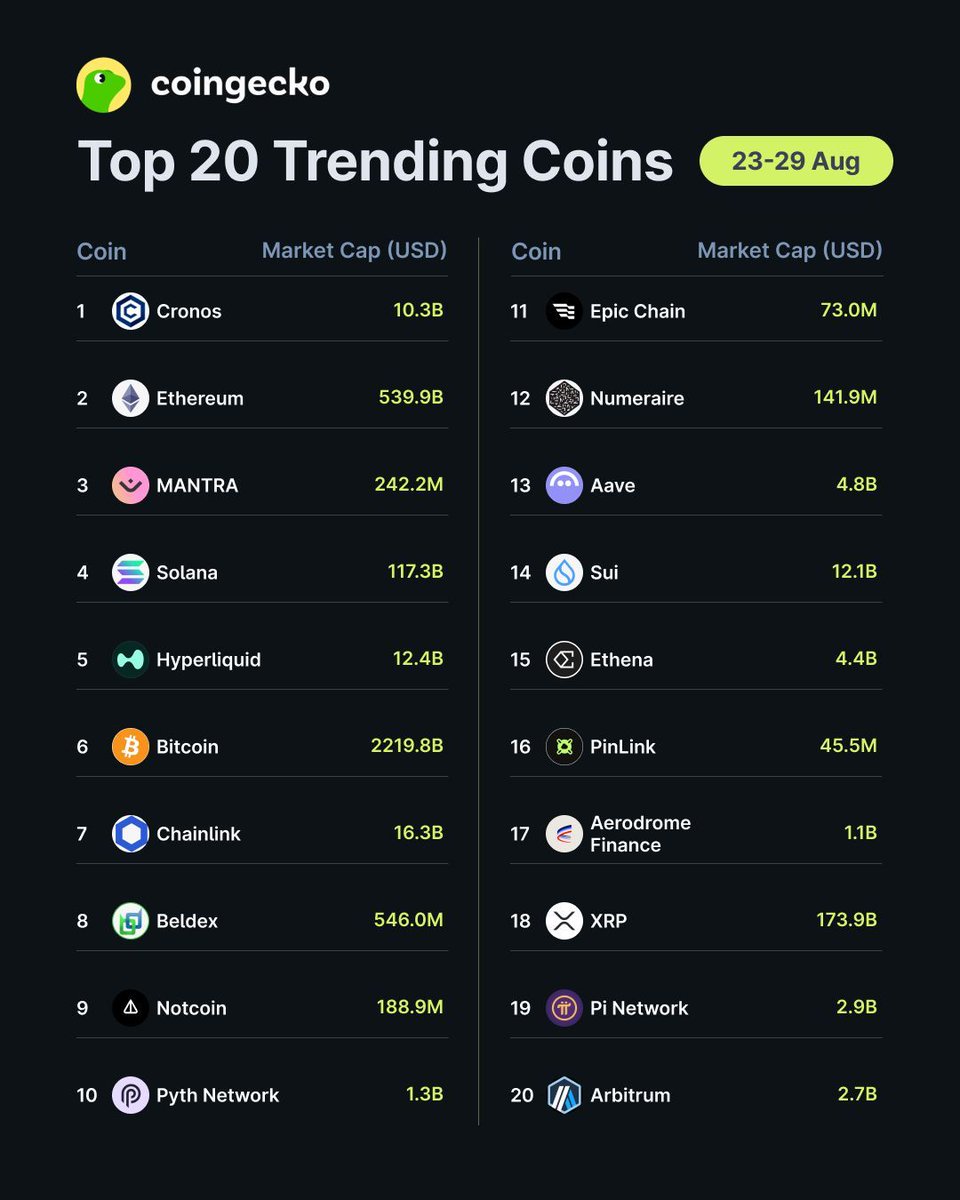
Prezzo: MantraDAO
in EUR

Informazioni su MantraDAO
Disclaimer
OKX non fornisce raccomandazioni su investimenti o asset. Devi considerare attentamente se il trading o l'holding di asset digitali è adatto a te alla luce della tua condizione finanziaria. Consulta un professionista legale/fiscale/finanziario per domande sulla tua specifica situazione. Per ulteriori dettagli, fai riferimento ai nostri Termini di utilizzo e all'Avviso di rischio. Utilizzando il sito web di terze parti ("TPW"), accetti che qualsiasi utilizzo del TPW sarà soggetto alle condizioni del TPW e disciplinato dalle stesse. Se non espressamente dichiarato per iscritto, OKX e i suoi affiliati ("OKX") non sono associati in alcun modo al proprietario o all'operatore del TPW. Accetti che OKX non è responsabile di eventuali perdite, danni e qualsiasi altra conseguenza derivanti dall'utilizzo del TPW. Tieni presente che l'uso di un TPW potrebbe comportare una perdita o una diminuzione dei tuoi asset. Il prodotto potrebbe non essere disponibile in tutte le giurisdizioni.
Prestazioni prezzo MantraDAO
MantraDAO sui social



Guide

Crea un conto OKX gratuito.
Finanzia il tuo conto.
Scegli la criptovaluta.
Domande frequenti relative al prezzo di MantraDAO
MANTRA è una piattaforma DeFi che si concentra su governance, staking, prestiti e molto altro. Funziona su Parity Substrate per Polkadot, con l'obiettivo di creare un ecosistema finanziario decentralizzato.
MANTRA utilizza una governance trasparente e offre diversi servizi DAO e DeFi, tra cui la gestione della liquidità, il launchpad, la governance DAO, lo staking, il lending e altro ancora, coinvolgendo gli utenti nel processo decisionale e nelle attività finanziarie.
Puoi acquistare token OM su una serie di mercati di trading di spot diversi. Un esempio è l'exchange di criptovalute OKX, che offreOM/USDTcoppia di trading.
Se desideri acquistare OM con valute fiat, OKX ha un Acquisto express opzione che ti sarà utile. La piattaforma ti consente anche di usareConvertifunzione per convertire i tuoi holding in eccesso in OM. In alternativa, se vuoi convertire OM in fiat, puoi usareCalcolatore di criptovalute OKXper controllare i tassi di conversione.
Esplora MantraDAO
Nel raggiungere la vera decentralizzazione, la costruzione della community è una pietra angolare essenziale. Questa comprensione ha incoraggiato la nascita diorganizzazioni autonome decentralizzate (DAO). Un esempio di questo concetto è MANTRA DAO, un componente integrale dell'ecosistema MANTRA.
Cos'è MANTRA
MANTRA (precedentemente noto come MANTRA DAO) è un gruppo governato dalla comunitàfinanza decentralizzata (DeFi)piattaforma specializzata in staking, prestiti egovernance. Funziona come un hub in cui la community non solo influenza i cambiamenti futuri del progetto attraverso il voto, ma anche riceve ricompense. Opera su Parity Substrate perPolkadotecosistema, MANTRA DAO mira a creare un ecosistema per il Web3 guidato dalla comunità, trasparente e decentralizzato per consentire alle persone con un controllo finanziario e una crescita del patrimonio collettivo.
Il team MANTRA
MANTRA è stata cofondata da Will Corkin, John Patrick Mullin e Rodrigo Quanı. Will Corkin è un imprenditore blockchain e fintech con un notevole background nei mercati di criptovalute e dei titoli tokenizzati. John Patrick Mullin offre esperienza come esperto in istruzione e tokenizzazione a Hong Kong. Rodrigoın, un ex bancario di investimenti con sede a Hong Kong, è passato alle tecnologie emergenti e ha fondato Moon Street Ventures.
Come funziona MANTRA
L'approccio di MANTRA si basa su un impegno dedicato al coinvolgimento della comunità. Questa dedizione si riflette in un meccanismo di governance trasparente che promuove l'unità e il processo decisionale collaborativo. In questo contesto, la piattaforma offre una diversificata gamma di servizi DAO e DeFi, progettati con cura per aumentare la sicurezza e presentare contemporaneamente percorsi per guadagnare. Questi servizi includono aspetti essenziali come gestione della tesoreria, launchpad e controllo delle emissioni, governance della DAO e sovvenzioni, tra le altre offerte.
Token di governance di MANTRA: OM
MANTRA DAO ha introdotto il suo token nativo, OM, a metà agosto 2020. Ha un'offerta massima di 888.888.888 token OM, equivalente alla sua offerta totale. OM ha diverse applicazioni come staking, yield farming, assunzione e concessione di prestiti, governance e voto.
Distribuzione OM
OM è distribuito nel modo seguente:
- L'85% destinato al pubblico con una vendita pubblica
- 9 percent distribuito tramite una vendita privata
- 17,5% mantenuto dal team e dai consulenti
- 30% destinato alle ricompense di staking
- 12,5% assegnato ai referral
- 10% destinato alla riserva
- Lo 12,5% è messo da parte per le sovvenzioni
Informativa ESG