APENFT价格
(美元)

了解APENFT
免责声明
请参阅我们的 使用条款 和 风险警告,了解更多详情。通过使用第三方网站(“第三方网站”),您同意对第三方网站的任何使用均受第三方网站条款的约束和管辖。除非书面明确说明,否则欧易及其关联方(“OKX”)与第三方网站的所有者或运营商没有任何关联。您同意欧易对您使用第三方网站而产生的任何损失、损害和任何其他后果不承担任何责任。请注意,使用第三方网站可能会导致您的资产损失或贬值。本产品可能无法在所有司法管辖区提供或适用。
APENFT 的价格表现
APENFT 社交媒体动态




快捷导航

APENFT 常见问题
APENFT 把艺术品以 ERC-721/TRC-721 标准铸造成链上代币。这些代币存储在 NFT 代币的 ERC-20/TRC-20 智能合约中,底层艺术品的权利将属于 NFT 持有者。
包含在铸造的 ERC-721/TRC-721NFT 代币中的数据,以及底层艺术品的记录永久存储在 BitTorrent 文件系统中,而文件存储在区块链上。
您可以在欧易交易所购买 APENFT 币对比如 NFT/USDT 交易对。或者您可以使用法币直接 购买 APENFT 或使用“闪兑”功能 将加密货币兑换成 APENFT。
在您开始与欧易交易所交易之前,您需要 注册一个交易账户。如果要用您选择的法币购买 APENFT ,请点击顶部导航栏“买币”下的“快捷买币”。如果使用 NFT/USDT 或 NFT/USDC 交易对或将加密货币转换 APENFT,请分别点击“交易”下的“基础交易”或“闪兑”功能将加密货币转换为 APENFT。
深度了解APENFT
APENFT 是一个基于 TRON-based 的平台,致力于让世界级艺术家可以自由的交易他们的艺术品 非同质化代币 (NFTs)。只需几下鼠标,该项目投资顶级非艺术平台和艺术品,孵化领先艺术家,组织艺术展览,就可以支持和发展 NFT 艺术生态系统。NFT 是 APENFT 的原生治理代币。
APENFT 的第一批藏品包括一些世界上最受欢迎的艺术家的作品,如巴勃罗·毕加索、安迪·沃霍尔、比普尔和帕克。APENFT 还宣布设立 1 亿美元的 NFT 游戏基金,用于投资高质量的 NFT 游戏、GameFi 和元宇宙项目,该基金由 SlowMist 提供担保。
APENFT 的另一个收入来源是咨询。该项目计划招募专业人士,指导政府机构、律师和行业精英影响非营利性行业增长的发展政策。
NFT 是 APENFT 的原生加密货币,允许持有者在 APENFT DAO 中对 NFT 艺术品的处理进行投票,并参与 APENFT 的活动。此外,通过参与 APENFT 治理、流动性空投和挖掘加密货币,在 justswap.org,justlend.org 和 sun.io,以及其他受支持的生态中,您将获得 NFT 以及 BTC, ETH,DOGE, TRX,BTT 等等代币奖励。
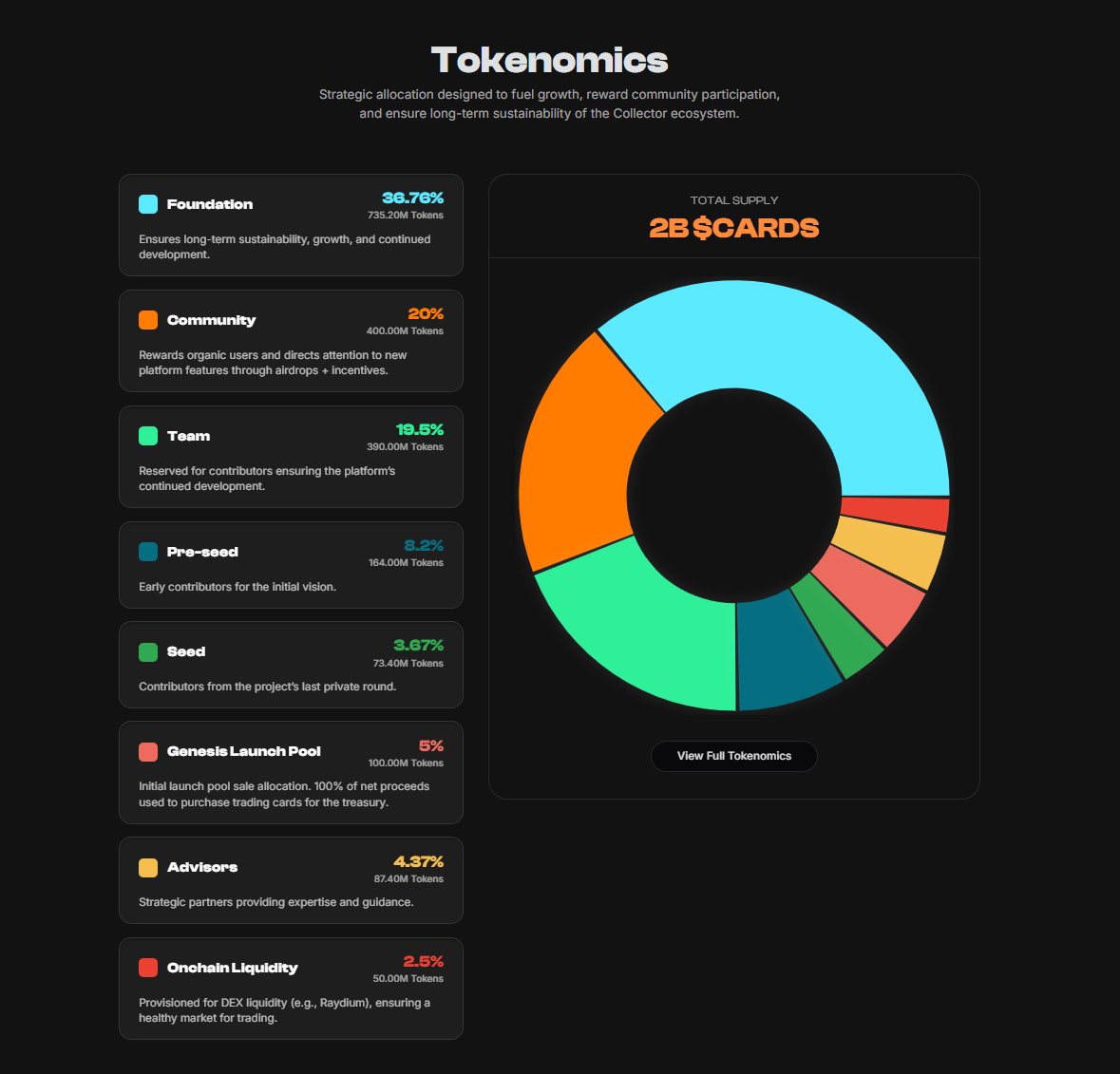
NFT 的价格及经济模型
NFT 是一个基于 tron 的令牌。它的总计划供应量为 9,999,900 亿枚代币。
其中 0% 的代币分配给合作艺术家,而 38% 的代币将分配给 DeFi 空投、矿池和 NFT 团队。在剩余的供应中,20% 将用于非生产性采购,10% 用于合作伙伴,2% 用于首次交易所上市。
NFT 的价格取决于 APENFT 平台的受众,以及 NFT 代币在其原生生态系统和加密市场中的应用。APENFT 计划促进顶级艺术品的创作和娱乐,与一线名人建立特许经营和定制非 ft 作品。对这些非功能性产品的需求将最终影响 NFT 的价格走势。
创始人团队
APENFT 于 2021 年 3 月 29 日在新加坡启动。
Steve Z. Liu,是 APENFT 的董事长,拥有 20 多年在主要金融机构工作的经验,如富达国际、所罗门美邦、野村国际和蚂蚁金服集团等。
APENFT 与佳士得 (Christie’s)、苏富比 (Sotheby’s) 和俏皮网关 (Nifty Gateway) 等全球最大拍卖行建立了合作关系;像毕普尔这样的流行艺术家;以及领先的艺术处理机构 Helu-Trans Group 等。此外,APENFT 还与 Tron Cool Cats 和 FansForever 建立了战略合作关系。
ESG 披露