SUI Ecosystem DEX #Cetus Is Code Security Audit Really Sufficient When Attacked?
The cause and impact of the attack on Cetus are not yet clear, but we can first take a look at the code security audit of Cetus.
For the uninitiated, we can't understand the specific technology, but this audit summary can be understood.
➤ Certik's audit
Certik's code security audit of Cetus found only 2 minor hazards that were resolved. There are also 9 informational risks, 6 resolved.
Certik gave an overall rating of 83.06 and a code audit score of 96.
➤ Other audit reports from Cetus (SUI Chain)
A total of 5 code audit reports are listed on Cetus' Github, excluding Certik's audit. It is estimated that the project team also knew that Certik's audit was a formality, so it did not include this report.
Cetus supports both Aptos and SUI chains, and the 5 audit reports are from MoveBit, OtterSec, and Zellic, respectively. Among them, MoveBit and OtterSec audit Cetus's code on the Aptos and SUI chains, respectively, and Zellic should also audit the code on the SUI chain.
Because it was Cetus on the SUI chain that was attacked this time, we will only look at the audit report of Cetus on the SUI chain below.
❚ Audit report from MoveBit
The report was uploaded to Github on 2023-04-28
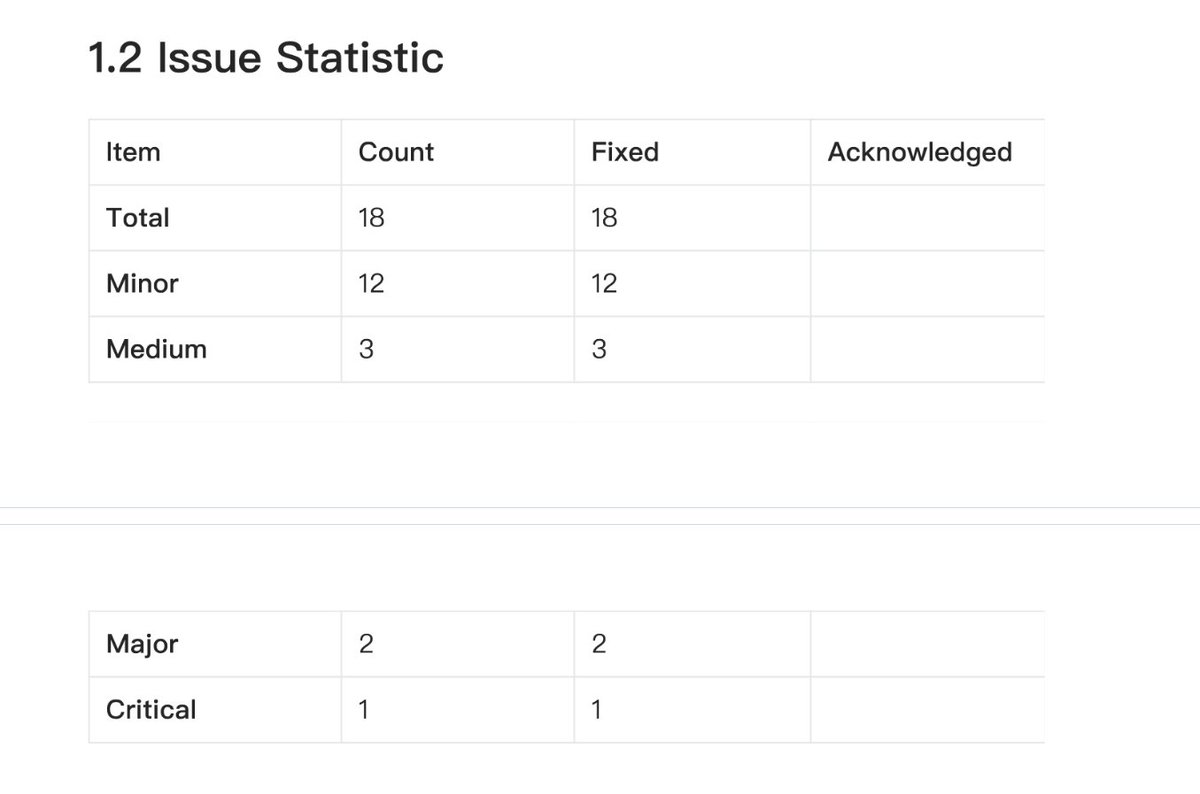
If we don't understand the specific content of the audit, we can find a table like this to see the number of risk issues listed in the report at each level, and how well they are resolved.
MoveBi's audit report on Cetust found a total of 18 risk issues, including 1 fatal risk issue, 2 major risk issues, 3 medium risk issues, and 12 mild risk issues, all of which have been resolved.
There are more problems than Certik has found, and Cetus has solved them all.
❚ Audit report from OtterSec
The report was uploaded to Github on 2023-05-12
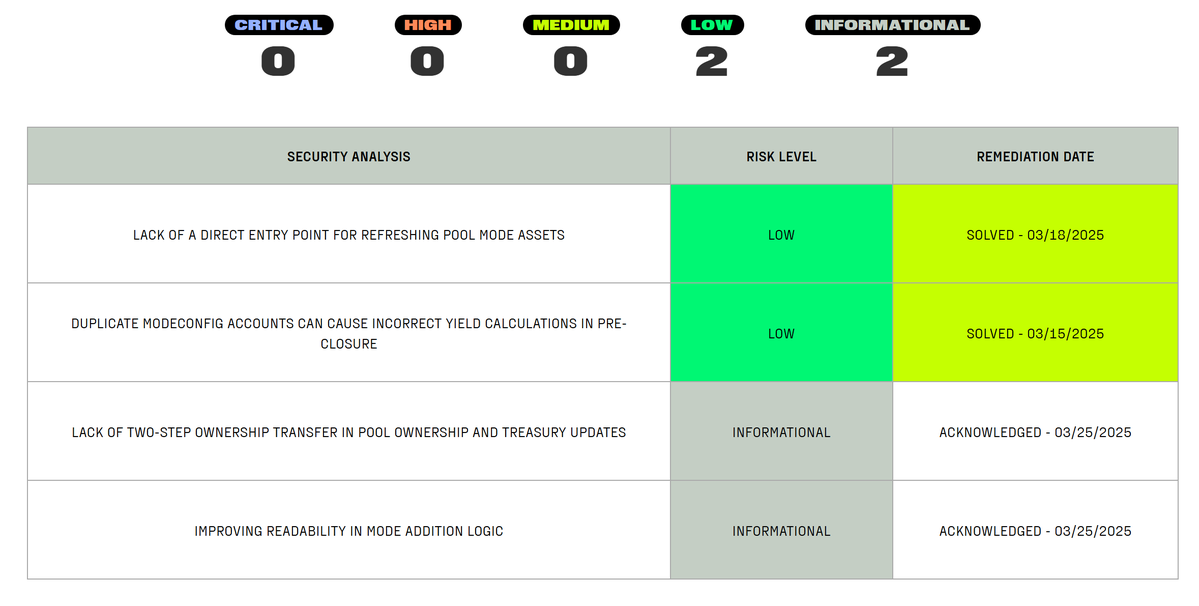
OtterSec's audit report on Cetus found a total of 1 high-risk issue, 1 medium-risk issue, and 7 informational risks, and the screenshots were not taken because the report table did not directly show the resolution of the risk issue.
Among them, both high-risk and medium-risk issues have been resolved. Informational risk issues, 2 resolved, 2 fixed patches submitted, and 3 more. After a rough study, these 3 are:
•The code of Sui and Aptos versions is inconsistent, which may affect the accuracy of price calculation of liquidity pools.
• Lack of paused state verification, no verification of whether the liquidity pool is in a paused state at the time of swap. If the pool is suspended, it may still be possible to trade.
• Convert U256 type to U64 type, if the value exceeds MAX_U64 it will cause overflow, which may lead to calculation errors in the case of large transactions.
It is uncertain whether the attack is related to the above issues.
❚ Audit report from Zellic
The report was uploaded to Github in April 2025
Zellic's audit report on Cetus identified three informational risks, none of which were fixed:
• A function authorisation issue that allows anyone to call to deposit fees into any partner account. It doesn't seem to be risky, it's saving money, not withdrawing money. So Cetus didn't fix it for the time being.
• There is a function that is still referenced by a deprecated generation, and the code is redundant, which seems to be risky, but the code is not prescriptive enough.
• One of the UI rendering issues in the NFT display data could have been character-based, but Cetus used the more complex TypeName data type in the Move language. This is not a problem, and it is possible that Cetus will develop other features for NFTs in the future.
Overall, Zellic found 3 ozone layer sub-issues, which are basically risk-free and belong to the code specification aspect.
We have to remember these three auditors: MoveBit, OtterSec, Zellic. Because most of the auditors on the market are good at EVM audits, these three auditors belong to the Move language code auditors.
➤ Audit & Security Level (Take the new DEX as an example)
First of all, projects that have not been audited by code are subject to a certain amount of Rug risk. After all, he is not even willing to pay for this audit, and it is difficult for people to believe that he has a desire to operate for a long time.
Secondly, Certik audit is actually a kind of "human audit". Why is it a "human audit", Certik has a very close cooperation with coinmarketcap. On coinmarketcap's project page there is an audit icon, which clicks on it to take you to Certik's navigation platform, skynet.
coinmarketcap, as a platform owned by Binance, indirectly enabled Certik to establish a partnership with Binance. In fact, Binance and Certik have always had a good relationship, so most projects that want to list on Binance will seek Certik's audit.
Therefore, if a project seeks Certik's audit, it is likely to want to list on Binance.
However, history has shown that the probability of an attack on a project audited only by Certik is not low, such as DEXX. There are even projects that have been FUG, such as ZKasino.
Of course, Certik also has some other security help, not only code auditing, Certik will scan websites, DNS, etc., and there are some security information other than code auditing.
Third, many projects will seek 1~more than one other high-quality audit entities to conduct code security audits.
Fourth, in addition to professional code audits, some projects will also carry out bug bounty programs and audit competitions to brainstorm and eliminate vulnerabilities.
Because this is a DEX product, let's take some newer DEXs as examples:
---------------------------
✦✦✦GMX V2 is a code audit conducted by 5 companies, including abdk, certora, dedaub, guardian, and sherlock, and launched a single bug bounty program of up to $5 million.
✦✦✦DeGate, a total of 35 companies from Secbit, Least Authority, and Trail of Bits conducted code audits, and launched a single bug bounty program of up to $1.11 million.
✦✦✦DYDX V4 is a code security audit conducted by Informal Systems, and a single bug bounty program of up to $5 million has been launched.
✦✦✦HyperLiquid conducts code security audits by HyperLiquid, and has launched a single bug bounty program of up to $1 million.
✦✦UniversalX is audited by Certik and another expert auditor (the official audit report has been temporarily removed from the shelves)
✦GMGN is special in that there is no code audit report found, only a single bug bounty program of up to $10,000.
➤ Write at the end
After reviewing the code security audits of these DEXs, we can see that even DEXs like Cetus, which are jointly audited by 3 auditors, are still vulnerable to attacks. Multi-agent audits, combined with vulnerability bounty programs or audit competitions, ensure relatively secure security.
However, for some new Defi protocols, there are still problems in code auditing that have not been fixed, which is why Brother Bee pays special attention to the code audit of new Defi protocols.
How safe are the DeFi projects that people are crazy about getting involved in their funds?
Safety is no small matter!
Especially for DeFi/PayFi/RwaFi products, where user funds are deposited or authorised, security is always the first and most important.
Mature DeFi products such as Uniswap, GMX, and DyDx have been tested by the market (hackers) for a long time, and their security is relatively higher.
However, there is a higher level of uncertainty in new DeFi applications. That's why, new DeFi products, will have a relatively higher yield or airdrop return. Because it's a risk compensation for early participants.
Although code security audits cannot fully guarantee its security, it can relatively ensure security. In this article, we will take a look at several new DeFi/PayFi/RwaFi ...... Security management such as code audit of similar products.
➤Huma @humafinance
❚ Project Introduction
Huma is a PayFi project based on the Solana ecosystem and Stellar, which aims to reinvent payments, yields, and financing on the blockchain.
❚ Ecological scale
At present, Huma is ahead of the TGE, and there is a cap on the size of funds for ecological participation.
According to Huma's official website, the protocol currently has a total active liquidity of $104 million and a total trading volume of $4.3 billion.
❚ Code auditor: Halborn
Founded in 2019, Halborn has audited the code of many similar projects such as public chains and DeFi, such as: Thorchain, Taiko, Core Chain, Story, Plume, Solayer, Zetachain, Avalanche, Persistenct, etc.
❚ Audit report
According to the audit report, Huma identified a total of 2 low-risk issues that have been resolved. 2 informational risks are known. No moderate or upper risk was identified.
❚ Bug bounties and security contests
In July 2026, Huma launched a $50,000 bug bounty program on the cantina platform.
Cantina is a Web3 security marketplace platform founded in 2023 that offers security services such as security contests, bug bounties, security reviews, and more. Well-known projects such as Uniswap, Morpho, Pendle, PancakeSwap, and others have launched bug bounty programs or security contests on them.
➤DefiApp @defidotapp
❚ Project Introduction
DefiApp is an aggregated DeFi based on chain abstraction, including spot swap, perpetual futures, and lending applications.
❚ Ecological scale
According to DeFillama, DefiApp has a 24-hour aggregate trading volume of $137.38 million. The highest daily aggregate trading volume was $225.76 million.
❚ Code auditors
The DefiApp documentation shows that different parts are audited by different agencies:
✦ Infrastructure Section: Sela
Sela is a cloud security services organisation whose partners include Microsoft, Google, AWZ, and Alibaba.
✦ Web Application Section: Halborn
✦ Smart contract part: Cantina
✦ Airdrop part: pashov
Pashov Audit Group is a blockchain security company that has audited projects such as DeFi, Gaming, and Chain Split, such as Sushi, 1inch, Aave, Ethena, Radiant, and more.
❚ Audit report
The code audit report link in the DefiApp documentation is linked to its Github, but the link cannot be opened, and no audit report can be found in its Github.
Not sure if you haven't completed your audit yet? Or has it not been submitted to Github yet? @defidotapp
On the websites of the listed auditors, only pashov's audit report on DefiApp, that is, the audit of the airdrop part, was found.
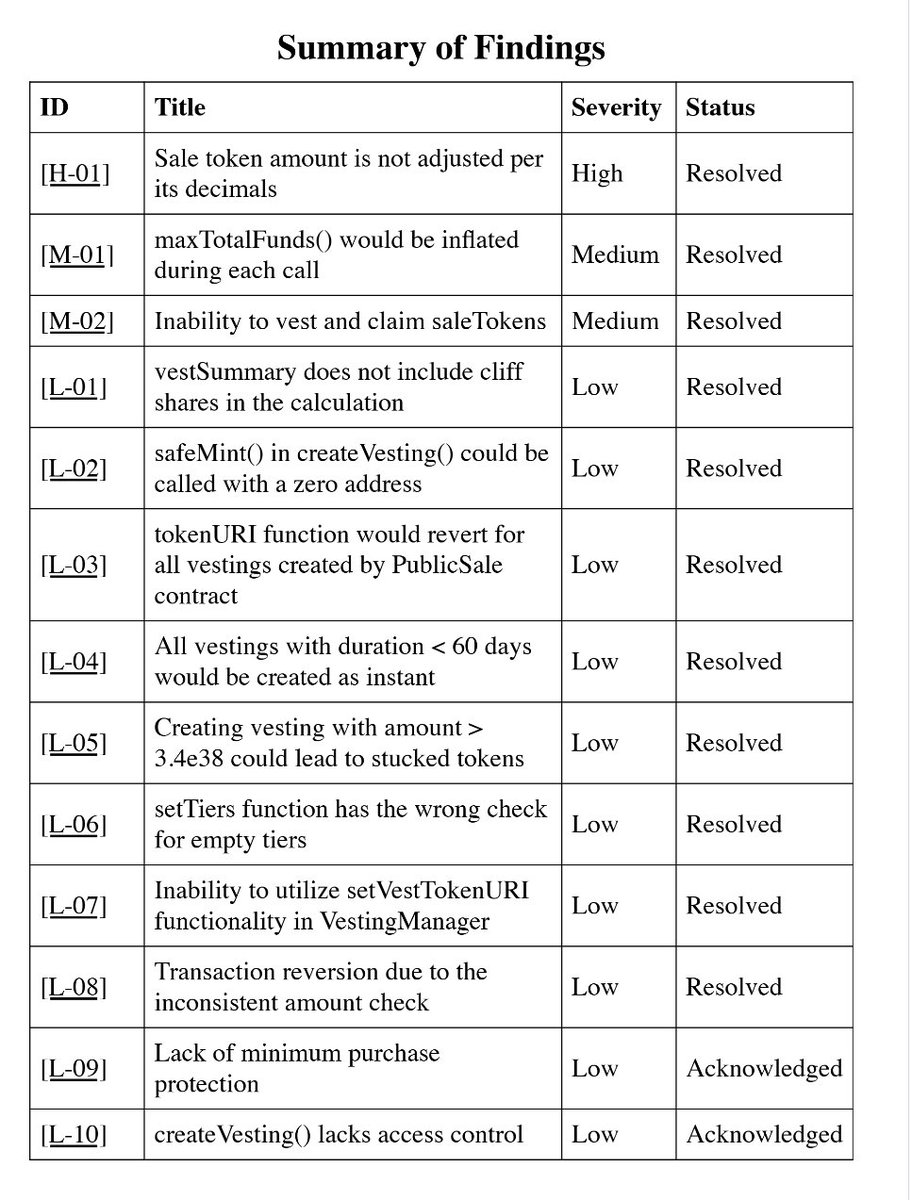
Pashov's audit report shows that DefiApp airdropped part of the code, and found a total of 1 high-risk, 2 medium-risk, and 10 low-risk. All but 2 low-risk issues were resolved.
➤StandX @StandX_Official
❚ Project Introduction
Perpetual futures DEX, currently known to support Solana and BSC chains.
❚ Ecological scale
According to StandX's official website, StandX has $TVL2297 million, a total of 30,468 transactions on the chain, and 7,798 active participants.
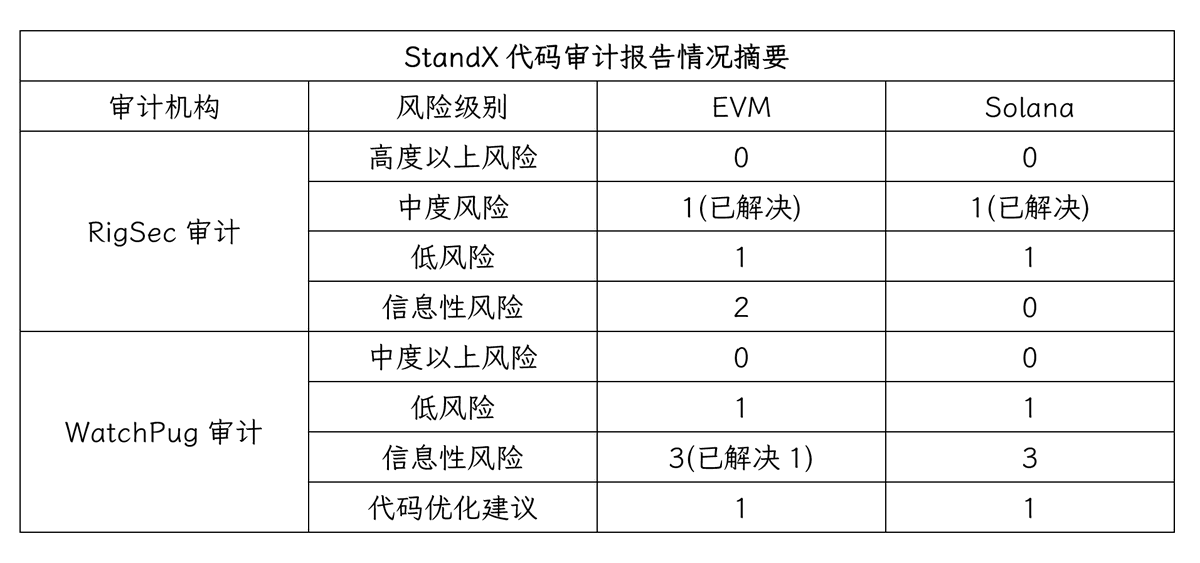
❚ Code auditors
StandX's code consists of two parts, the EVM chain and the Solana edge, all of which are double-audited by RigSec and WatchPug.
RigSec is a company focused on digital asset security, and its main market is currently in Asia, and its audited projects include edgeX Exchange.
WatchPug is a blockchain security audit company focused on code auditing of DeFi protocols, NFT projects, and Web3 applications. Audited projects include Equilibria Finance, Penpie, and others.
❚ Audit report
StandX's solana and EVM chaincode were audited by 2 auditors, and the report showed that all moderate or higher risks were addressed. There are several low-risk, informational risks, and code optimisation recommendations.
➤ Write at the end
Overall, Huma is a bit more secure. Not only is the risk level found in the code audit report lower, but the bug bounty program has been running for nearly one year. This may explain why Huma fills up in less than 1 hour every time Huma develops a deposit. The security awareness of large funds is still relatively high.
StandX's 4 audit reports show that the risk level is relatively low and above moderate is resolved. However, the two code audit companies that conducted the audit are relatively well-known, and there is a certain uncertainty about the security of StandX.
As for DefiApp, it is possible that the audit speculation of other parts except for the airdrop contract may not be completed yet. Or maybe the audit has been completed and the team is working on a fix for the issue.
Finally, for a new DeFi product, even if it passes a code security audit, it still can't be sure that it is fully secure.
Remind everyone to be cautious when participating in early Defi projects, and be even more cautious in operation!
39
33.6K
The content on this page is provided by third parties. Unless otherwise stated, OKX is not the author of the cited article(s) and does not claim any copyright in the materials. The content is provided for informational purposes only and does not represent the views of OKX. It is not intended to be an endorsement of any kind and should not be considered investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell digital assets. To the extent generative AI is utilized to provide summaries or other information, such AI generated content may be inaccurate or inconsistent. Please read the linked article for more details and information. OKX is not responsible for content hosted on third party sites. Digital asset holdings, including stablecoins and NFTs, involve a high degree of risk and can fluctuate greatly. You should carefully consider whether trading or holding digital assets is suitable for you in light of your financial condition.

