How scary is misusing AI? Both CZ and Vitalik have the potential to become brothers
Let's cut from this article... 💀 Creators, do you really know what you're writing?
Having said that, I chose this article simply because I felt that there were too many mistakes, and I believe that using AI to orchestrate content and process information is definitely a work that most people will use
Fake news is deliberately interspersed with real content to convince readers that it is true, which is the most lethal problem for current AI users, and it can cause far more problems than you think, as described in the following paragraph
It was an interesting feature that I saw the @Mira_Network team working on at the time
He was able to use AI to process the data to render a "everything you say is right" result, as in the following paragraph
"In addition, Changpeng 'CZ' Zhao has publicly acknowledged Vitalik Buterin's key role in shaping the cryptocurrency industry, which further cements their family-like relationship. This recognition goes beyond pure professional respect and points to a deeper kinship, emphasizing that they are brothers in the battle for cryptocurrency adoption and innovation."
In fact, if you are speculating in coins and paying attention to the market, you will also find that there are several projects called Spark recently, which make us all think that @0x_xifeng has started a 😂 business. Just kidding
But through this content, you can actually find out that he accidentally mixed up the two projects...
Originally, you may have to start DeFi projects, but they are all writing BTC? (Not to mention why there is this picture)
💡 @buildonspark is a BTC layer 2 that enables low-cost self-custody transactions of bitcoins and tokens, allowing users to simply use the Lightning Network to send and receive tokens locally
Follow the CT tweet and you can find keywords such as $FSPKS, LRC20, etc
💡 @sparkdotfi Spark Protocol, I think that's what he wants to introduce, is a completely different protocol, and old DeFi players must know that Spark Protocol, developed by the MakerDAO team, is a decentralized lending marketplace where users can use assets such as ETH, stETH, and sDAI to collateralize and lend DAI borrowing, and the current TVL is also very high
Frankly, if you've looked at the account information or rootdata of the above two projects, you can tell the difference, but there will be such a tweet that it is obvious that the author has not proofread it, and the person who left it has not raised any questions
So I thought it would be necessary for me to jump out and talk to you about this phenomenon
I also think that we must pay attention to various AI-related ecosystems for data verification, as long as there are some applications that can get out of the circle, AI networks can certainly be more valuable
---
Looking back, I would like to share the recent development of @Mira_Network, not only was I selected for @CBinsights's 2025 AI 100 team along with many well-known AI companies a while ago
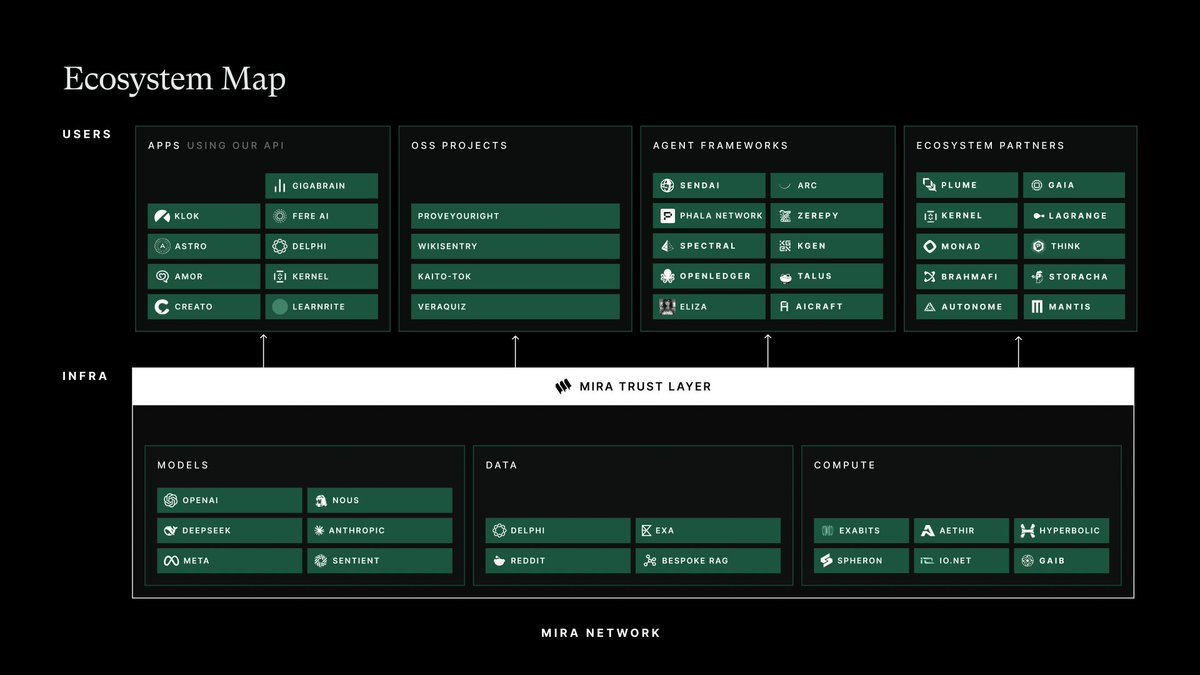
The ecosystem is also gradually expanding, and they just released their own ecological map 👀 tonight
It can be divided into the "user layer" and the "Infra layer".
Classification of user layers: teams using the Mira API, open source projects, AI proxy frameworks, ecosystem partners
There are a few of them that you are familiar with and that I have mentioned earlier
Contains @sendaifun @PhalaNetwork @plumenetwork @kernel_dao @monad_xyz @lagrangedev
The part of the Infra layer includes AI model providers, data sources, computing resource provision, etc
@NousResearch @deepseek_ai @SpheronFDN @gaib_ai @AethirCloud @hyperbolic_labs
I think all of the above protocols can be followed, the journey of development may take time, but it is definitely worth paying attention to



There is no intention of going to war, just to make this environment better, to encourage it
🍕How Spark works
@sparkdotfi is a decentralized off-chain Layer 2 (L2) solution for Bitcoin that is very different from traditional sidechain or rollup schemes.
Instead of relying on new blockchains, validators, or smart contracts, it employs a Bitcoin-based multi-signature sharing protocol that enables efficient transactions through multi-party collaboration to sign off-chain state updates, while anchoring security firmly on Bitcoin's Layer 1 (L1).
Spark doesn't require the introduction of a new consensus mechanism, a dedicated miner or block producer, and no native token to pay gas fees or transaction fees.
It leverages the Bitcoin network directly as the final settlement layer and seamlessly interoperates with the Lightning Network to become a fast and flexible off-chain execution layer, bringing unprecedented functionality expansion to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
🍖 Technical mechanisms
When a user deposits Bitcoin (BTC) into Spark, the funds are locked in a special multisig output on Bitcoin L1, typically a 2-of-2 multisig that is jointly controlled by the user and the Spark operator.
This deposit is mapped to "virtual BTC" on the Spark network at a 1:1 ratio, without the need for cross-chain bridges or wrapped tokens (such as WBTC).
Subsequently, users can off-chain these virtual BTC to other users on Spark in near real-time (typically within a second) by co-signing a new UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) ownership allocation with the Spark operator.
Each Spark transaction is essentially a status update and requires the signature of the current owner and at least one operator to be valid.
This mechanism is highly similar to that of a state channel or state chain:
Funds are locked on-chain, but are quickly transferred through off-chain signatures until users choose to redeem their funds on the Bitcoin mainnet.
This design retains the decentralized nature and security of Bitcoin, while significantly improving the speed and efficiency of transactions.
🍟 Core Benefits:
Spark's architecture offers several benefits:
1. Instant transactions with near-zero cost
Spark supports instant transactions without waiting for block confirmations, and internal L2 transactions are completely free.
Users don't have to pay any fees to transfer BTC or tokens on Spark, as these transactions don't take up block space in Bitcoin L1 and are only subject to standard Bitcoin network fees when depositing or withdrawing.
Lightspark has confirmed that Spark internal transactions are fee-free, and that when users send BTC to the Lightning Network via Spark, they will only be charged a 0.25% conversion fee plus possible Lightning Network routing fees to compensate operators for inter-network conversion costs.
This low-cost nature makes Spark an efficient payment and asset transfer platform.
2. Offline payment reception
Spark breaks through the limitations of traditional Bitcoin L1 and the Lightning Network to support offline payment acceptance.
In the Lightning Network, the receiver must be online to sign the channel update, while Spark allows UTXO ownership to be unilaterally redistributed off-chain and complete the transaction.
This means that users can send Bitcoin to offline Spark users, and when the receiver comes back online, the balance will be updated with a transaction co-signed by the operator, which will be available immediately.
This feature opens up new possibilities for Bitcoin payment scenarios, such as the reliable transfer of funds even in an unstable network environment.
3. Unilateral exit with user control
Spark uses a 2-of-2 multisig model to ensure that users always have full control over their funds.
Even if the Spark operator refuses to cooperate or tries to review the transaction, users can unilaterally withdraw funds on Bitcoin L1 through a pre-signed close-transaction or time-lock mechanism.
This non-custodial design eliminates reliance on Lightspark or other third parties, significantly reducing counterparty risk and keeping user funds safe.
🍿 Current networks and future developments
At present, the Spark network is jointly signed by two operators, Lightspark and Flashnet, which has certain centralization risks:
If both carriers are offline at the same time, new transactions on Spark will be temporarily suspended.
However, user funds are always safe and can be retrieved through the on-chain unilateral withdrawal mechanism.
Lightspark has said that it will introduce more operators in the future to gradually enhance the decentralization and resilience of the network, with the goal of achieving a distributed model similar to the Lightning Network, allowing multiple operators to operate according to the rules of the protocol while providing a simpler and more intuitive user experience.
🌭 Practical application and ecological integration
It's worth mentioning that industry giants such as Coinbase and Revolut have adopted Lightspark's infrastructure to run on the Lightning Network.
Extending to Spark is a natural evolution of these platforms, offering more robust self-custody, instant trading, and multi-asset backing.
Spark's interoperability makes it a bridge between the Bitcoin mainnet, the Lightning Network, and other blockchain ecosystems, providing users and businesses with a seamless payment and asset management experience.
🥓LRC20 token standard
LRC20 is one of the core innovations of the Spark ecosystem, launched in mid-2024 and is a native token protocol designed specifically for Bitcoin L2.
Through Spark, LRC20 allows users to issue digital tokens registered on the Bitcoin blockchain and managed off-chain, introducing a diverse range of asset types to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
🥨 Technical implementation
To create an LRC20 token, a transaction is executed on Bitcoin L1 that embeds metadata via OP_RETURN fields, including the token's unique ID, name, total supply, and number of decimal places.
This transaction serves as a "genesis record" for the token, pegging it to Bitcoin L1 and completing the official registration.
Once the transaction is confirmed, the Spark protocol recognizes the token, allowing the creator to mint the initial supply on Spark.
All subsequent minting and transfer operations take place in Spark's off-chain environment, and transactions are instant and fee-free, consistent with native BTC transfers on Spark.
Bitcoin L1 acts as a public registry that ensures the transparency and immutability of tokens, while Spark acts as an efficient operational layer that is responsible for the rapid transfer and management of tokens.
🥐LRC20 features
LRC20 is designed for stablecoins and regulated asset issuers, and unlike Ethereum's ERC-20 standard, it does not support permissionless fair distribution (like ICOs).
Only the address of the token creator can mint additional tokens, and other users need to receive tokens in the form of creator distribution (airdrops, sales, etc.).
The LRC20 has built-in compliance features, including:
1. Freezing Mechanism:
Creators can freeze tokens from any address, preventing them from being transferred or received until they are unfrozen.
2. Destruction Mechanism:
Creators can burn their own tokens, and the destruction is irreversible.
These features introduce a degree of centralization, but are essential for stablecoin issuers that need to meet regulatory requirements, such as Tether or Circle.
LRC20 provides a Bitcoin-native solution that doesn't need to rely on Ethereum or other blockchains.
🍗 Interoperability & Use Cases
As of mid-2025, LRC20 operates only on the Spark network, relies on the Spark protocol, and cannot be transferred directly on the Bitcoin mainnet.
However, through Spark's interoperability with the Lightning Network, LRC20 tokens can participate in Lightning Network payments through atomic swaps.
For example, a user can pay for a Lightning Network invoice with an LRC20 stablecoin (such as USDB), which the Spark operator converts to BTC in the background and sends to the receiver, who completes the payment in the stablecoin.
This mechanism enables Spark users to seamlessly interact with the Bitcoin ecosystem while holding non-BTC assets.
LRC20 brings native tokenization capabilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem, expanding the possibilities from stablecoins, loyalty points, to tokenization of real-world assets.
It lays the foundation for Bitcoin's native DeFi ecosystem, supporting decentralized exchanges (DEXs), NFT marketplaces (with the undivided LRC20 token as NFTs), governance tokens, and even complex financial applications such as lending and derivatives that may be involved in the future.
🥩The team behind Spark
Spark was developed by Lightspark, a company founded in 2022 to unlock the full potential of Bitcoin as a global payment network.
David Marcus, co-founder and CEO of Lightspark, was president of PayPal and vice president of Facebook, led Messenger and co-founded the Libra (later renamed Diem) cryptocurrency project.
He works with a team of industry veterans, including:
Kevin Hurley (Co-Founder & CTO)
Tomer Barel (Operating Partner, PayPal and Diem)
Christian Catalini (Chief Strategy Officer, Co-Author, Libra)
Team members also include technical experts from companies like Xapo, Stripe, Square, and Coinbase.
Known as the "PayPal mafia" and the Libra project, this elite team has demonstrated a strong ability to integrate cryptocurrencies with traditional finance.
Lightspark raised more than $170 million in a Series A funding round led by top venture capital firms such as a16z, Paradigm, Coatue, Thrive Capital, Ribbit Capital, and more.
This huge funding round reflects investors' unwavering confidence in Bitcoin's potential:
Through innovations such as Spark, Bitcoin is not only a store of value, but also a core protocol for global internet payments, enabling self-custodial, near-instant, multi-asset transactions, all backed by Bitcoin's unmatched security.
#SNAPS
@Cookie3_com #SparkFi @cookiedotfun




69
281.05K
The content on this page is provided by third parties. Unless otherwise stated, OKX is not the author of the cited article(s) and does not claim any copyright in the materials. The content is provided for informational purposes only and does not represent the views of OKX. It is not intended to be an endorsement of any kind and should not be considered investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell digital assets. To the extent generative AI is utilized to provide summaries or other information, such AI generated content may be inaccurate or inconsistent. Please read the linked article for more details and information. OKX is not responsible for content hosted on third party sites. Digital asset holdings, including stablecoins and NFTs, involve a high degree of risk and can fluctuate greatly. You should carefully consider whether trading or holding digital assets is suitable for you in light of your financial condition.


